c语言sscanf函数的用法是什么
506
2022-11-25
SpringMVC @RequestBody的使用解析
目录SpringMVC @RequestBody的使用@RequestBody使用的一些注意事项
SpringMVC @RequestBody的使用
Spring mvc是一个非常轻量的mvc框架,注解可以大大减少配置,让请求的拦截变得比较简单。这次记录下@RequestBody 注解接收参数尤其是数组参数的用法。
关于容器的配置不再多说,这里写出spring-servlet.xml的sechme:
xmlns:xsi="http://w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:p="http://springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:mvc="http://springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:task="http://springframework.org/schema/task" xsi:schemaLocation="http://springframework.org/schema/context http://springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd http://springframework.org/schema/beans http://springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://springframework.org/schema/mvc http://springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.0.xsd http://springframework.org/schema/task http://springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task-4.0.xsd">
xmlns:xsi="http://w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:p="http://springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:mvc="http://springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:task="http://springframework.org/schema/task"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://springframework.org/schema/context
http://springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd
http://springframework.org/schema/beans
http://springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.0.xsd http://springframework.org/schema/task http://springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task-4.0.xsd">
只要对应包名下面的添加注解即可扫描到对应的控制器,一般采用@Controller
RequestBody接收基本类型
@Controller
public class TestController {
// url请求拦截
@RequestMapping("test/test.do")
@ResponseBody // 返回参数为jsON
public void test(@RequestBody String name) {
System.out.println("getParams : " + name);
}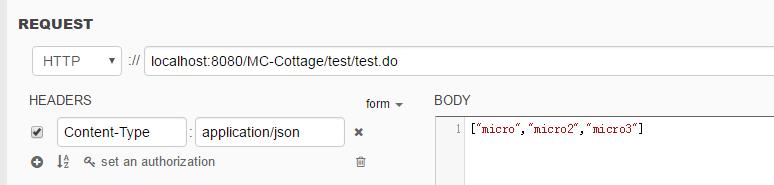
}
@RequestBody只要接收POST请求Body里的数据。
这样发送请求,即可在java控制台中打印:
getParams : {"name":"micro"}
@RequestBody接收基本数组
然后我们接收基本类型数组:
@RequestMapping("test/test.do")
@ResponseBody
public void test(@RequestBody List
System.out.println("getParams : " + nameList);
}
这样即可获取到参数,不要body里写成了{“nameList”:[“name1”,“name2”]}这样会抛出异常。
@RequestBody是对应的POST请求的body,body即是获取的参数,如果想通过参数去获取,则要使用@RequestParams 注解:
@RequestMapping("test/test.do")
@ResponseBody
public void test(@RequestParam("name") String name) {
System.out.println("getParams : " + name);
}
注意是GET请求,参数直接放到URL后面,这样就可以使用@RequestParams获取到对应参数名的参数值。如果是复杂的对象。
@RequestBody的使用。
定义model:
class Person {
private Long id;
private String name;
// setter getter
}
@RequestBody接收复杂对象
接收参数的方式
@RequestMapping("test/test.do")
@ResponseBody
public void test(@RequestBody Person person) {
System.out.println("getParams : " + person.getId() + " ," + person.getName());
}
即可获取到参数,body里的参数会自动匹配到person的属性并赋值。
注意名字要与对象的属性变量名一致。否则获取不到参数,例如这里就不能在body里写成{“i”:1,“name”:“micro”},这样获取到person的id为null。
@RequestBody接收复杂对象数组
如果是复杂对象数组:
@RequestMapping("test/test.do")
@ResponseBody
public void test(@RequestBody List
for (Person p : personList) {
System.out.println(p.getId() + " ," + p.getName());
}
}
请求方式如下,注意body里的格式是[]数组。
控制台打印:
1 ,micro
2 ,micro2
即完成了@RequestBody接收各种类型的参数。
@RequestBody使用的一些注意事项
众所周知,springmvc中@RequestBody的注解是一个很实用的功能,它能帮我们解析客户端(移动设备、浏览器等)发送过来的json数据,并封装到实体类中。
但我今天要说的不是它的原理,而是记录一些工作中使用@RequestBody注解遇到的一些问题,也提醒广大java开发者避免类似的问题。
最近有个需求,接收客户的设备发送过来的json数据,客户的设备里面只能修改ip,然后通过http协议的post方式发送数据过来。我很自然地想到在登录页那里处理,在toLogin方法中增加@RequestBody Kehu kehu参数,用户解析并封装json数据。
废话不多说,上代码,如下所示:
@RequestMapQUMPeping(value = "/toLogin")
public ModelAndView toLogin(HttpServletRequest request, @RequestBody Kehu kehu) throws Exception {
// 接收客户设备发送过来的json数据
if (kehu != null && !StringUtil.isEmpty(kehu.cmd)) {
uploadData(kehu);
}
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
PageData pageData = this.getPageData(request);
pageData.put("SYSNAME", Tools.readTxtFile(Const.SYSNAME)); // 读取系统名称
mv.setViewName("base/login");
mv.addObject("pd", pageData);
return mv;
}
一切看似很完美,在浏览器上测试一下,输入localhost(我的项目已经设置为了缺省项目,端口号也改为了80)
我傻眼了,报了400错误。如下图所示:
The request sent by the client was syntactically incorrect.
翻译过来就是:客户端发送的请求在语法上是不正确的。
没加@RequestBody Kehu kehu之前是正常的,问题肯定出在了这里。我一看RequestBody的源码:
package org.springframework.web.bind.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter;
/**
* Annotation indicating a method parameter should be bound to the body of the web request.
* The body of the request is passed through an {@link HttpMessageConverter} to resolve the
* method argument depending on the content type of the request. Optionally, automatic
* validation can be applied by annotating the argument with {@code @Valid}.
*
*
Supported for annotated handler methods in Servlet environments.
*
* @author Arjen Poutsma
* @since 3.0
* @see RequestHeader
* @see ResponseBody
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter
*/
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RequestBody {
/**
* Whether body content is required.
*
Default is {@code true}, leading to an exception thrown in case
* there is no body content. Switch this to {@code false} if you prefer
* {@code null} to be passed when the body content is {@code null}.
* @since 3.2
*/
boolean required() default true;
}
required方法默认返回值是true。
这样问题就明朗了,我请求localhost的时候,没有传json过去,所以就会报400错误,因为客户端发送的请求在语法上是不正确的。
解决方法:在@RequestBody后面加上(required=false)就可以了。表示kehu对象可以不传入。
/**
* 访问登录页
* @RequestBody(required=false) 表示kehu对象可以不传入。
* 一定要加上required=false,否则登录的时候会报400错误。错误代码:
* The request sent by the client was syntactically incorrect.
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/toLogin")
public ModelAndView toLogin(HttpServletRequest request, @RequestBody(required=false) Kehu kehu) throws Exception {
// 接收硬币机发送过来的json数据
if (kehu != null && !StringUtil.isEmpty(kehu.cmd)) {
uploadData(kehu);
}
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
PageData pageData = thQUMPeis.getPageData(request);
pageData.put("SYSNAME", Tools.readTxtFile(Const.SYSNAME)); // 读取系统名称
mv.setViewName("base/login");
mv.addObject("pd", pageData);
return mv;
}
版权声明:本文内容由网络用户投稿,版权归原作者所有,本站不拥有其著作权,亦不承担相应法律责任。如果您发现本站中有涉嫌抄袭或描述失实的内容,请联系我们jiasou666@gmail.com 处理,核实后本网站将在24小时内删除侵权内容。
发表评论
暂时没有评论,来抢沙发吧~